ABOUT US
RESEARCH
SCIENTISTS
INT'L COOPERATION
EDUCATION
New review in enhancing the critical performance of Deep-UV frequency-doubling crystals with covalent tetrahedra
Editor: | Jun 23,2021
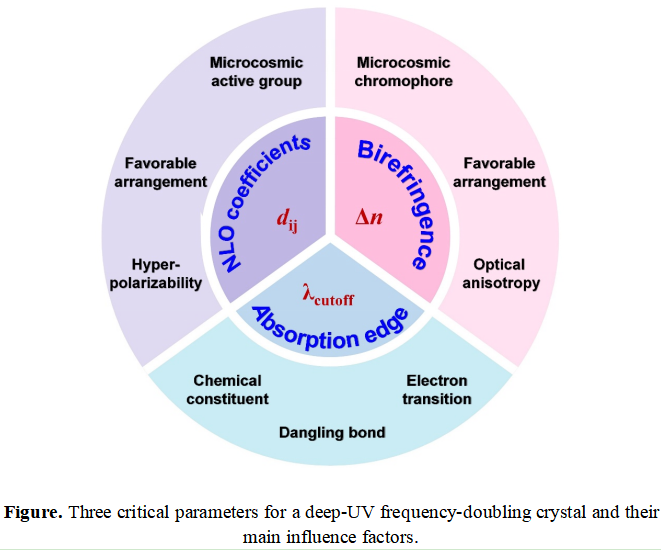
Deep-ultraviolet (deep-UV, λ < 200 nm) coherent light is emerging as an indispensable driving force behind the innovation of optics and materials science. The deep-UV-driven applications range from laser interference photolithography to precise micromachining to futuristic ideas such as space propulsion using remotely controlled positioning lasers. Unlike conventional approaches to obtaining deep-UV light, for instance, synchrotron radiation, direct laser excitation, and gas discharge, nonlinear frequency conversion can be regarded as a more attractive way to endow such resource with high photon energy, high photon flux, and high spectral resolution. Actually, the nonlinear frequency conversion can be efficient only with the use of high-performing frequency-doubling crystals, which should be well-suited to the physics of nonlinear optical process. However, the necessary prerequisites for a practical frequency-doubling crystal are extremely strict, and thus very few crystals can be used to generate the deep-UV light. Faced with this, sustained effort has been expended by chemists and materials scientists toward discovering novel deep-UV frequency-doubling crystals. Studies have so far indicated that the main difficulty in finding a perfect candidate comes from the combination of three critical properties (absorption edge, nonlinear optical coefficients, and birefringence) into one crystal because they share the mutual relation of restriction and influence.
Recently, a research group led by Prof. Shilie Pan at Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Science, has present the recent progress in discovering emergent deep-UV frequency-doubling crystals with the discussion of recent efforts to balance the three critical properties by introducing the covalent tetrahedra. The review was published in Accounts of Material Research with title of “Toward the Enhancement of Critical Performance for Deep-Ultraviolet Frequency-Doubling Crystals Utilizing Covalent Tetrahedra”.
In this review, the followings are shown to be effective to achieve the tnhancement of critical performance for deep-ultraviolet frequency-doubling crystals: (i) elimination of dangling bonds with covalent tetrahedra to push the absorption edge of crystals into the deep-UV spectral region; (ii) orbital hybridization enhancement, charge-transfer energy reduction, and symmetry breaking of original tetrahedra with the introduction of X atoms and thereby the achievement of the enhancement of nonlinear optical coefficients; and (iii) uniform alignment of tetrahedral distorted units and the introduction of polarized X atoms containing [MO4–nXn] tetrahedra with high polarizability anisotropy to cause the large enhancement of birefringence. These findings allow us to understand the microcosmic behaviors of covalent tetrahedra on pushing the current limitations and provide an optional functional group toward the maximum thresholds of three critical parameters for deep-UV frequency-doubling crystals.
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China, National Key Research Project, and Xinjiang Key Research and Development Program.
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/accountsmr.1c00028
附件下载:
 (86) 991-3838931
(86) 991-3838931 lhskj@ms.xjb.ac.cn
lhskj@ms.xjb.ac.cn (86)991-3838957
(86)991-3838957 40-1 Beijing Road
Urumqi, XinjiangChina
40-1 Beijing Road
Urumqi, XinjiangChina
