Researchers Revealed the Potential Use of Chickpea Sprouts Isoflavone Extract for the Treatment of Diseases Caused by Estrogen Deficiency
Editor: | May 19,2013
Peri- and postmenopausal syndromes in middle-aged and elderly women are marked by brief flushes, mood swings, dry skin, sleep disorders and joint pain, which are closely related to the lack of ovarian hormones. A significant decrease in estrogen levels in women during the menopausal period also causes osteoporosis, become a major public health concern.
Researchers from Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences found the estrogenic activities of the isoflavones extracted from chickpea sprouts (ICS) in ovariectomized rats, and it has the potential use of ICS for the treatment of menopausal symptoms and osteoporosis caused by estrogen deficiency.
Cicer arietinum L. is one of the oldest and most widely planted legumes in the world. Its common name (chickpea) was derived because its seed is spiry, like an eagle’s beak.It is also an important food for its rich in high-quality protein, carbohydrates and essential mineral elements.
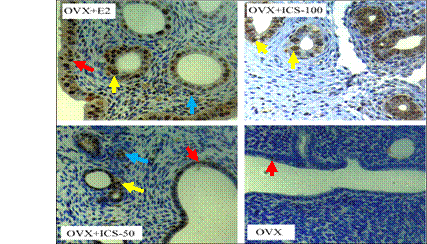 |
| Immunohistochemical analysis of PCNA expression in uteri of OVX rats. Representative micrographs of PCNA expression (brown staining in nuclei) in uteri of OVX+E2, OVX+ICS-50, OVX+ICS-100, and OVX+Veh rats. The color arrows were indicated the positive nuclei in different cells: luminal epithelial cells (red arrows), glandular epithelial cells (yellow arrows) and stromal cells (blue arrows) in uterine (×400). (Imaged by XTIPC) |
“Our study shows for the first time that ICS exhibits strong estrogenic activity and prevents bone loss in OVX rats” said Prof. Haji Akber AISA, the study's lead author. These results indicate that ICS is beneficial for the treatment of menopausal symptoms and osteoporosis caused by estrogen deficiency.
The results have been published on Acta Pharmacological Sinica 34, 380-386 (March 2013).
This work was supported in part by grants from the China National Funds for Distinguished Young Scientists, National Natural Science Foundation of China etc.
Contact: Haji Akber AISA
E-mail: haji@ms.xjb.ac.cn
Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences
附件下载:
 (86) 991-3838931
(86) 991-3838931 lhskj@ms.xjb.ac.cn
lhskj@ms.xjb.ac.cn (86)991-3838957
(86)991-3838957 40-1 Beijing Road
Urumqi, XinjiangChina
40-1 Beijing Road
Urumqi, XinjiangChina