Reviews on Cellulose-based Fluorescent Materials for Chemical Sensing
Editor: | Feb 28,2025
In recent years, the advancement of environmentally high-response sensing materials has attracted great attention for their highly sensitive and selective analytical properties and instrument-free portable applications. As one of the most abundant and widely used raw materials on earth, through chemical bonding, self-assembly and coordination, cellulose could endow fluorescent sensing materials with the advantages of ease of fabrication and economical advantage in preparation, multi-functionality and security in utilization, and renewability and biodegradability in post-consumption processing. Towards a reasonable design and utilization of cellulose and its derivatives within the domain of fluorescent sensing, Prof. DOU Xincun's lab at Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry (XJTIPC) of Chinese Academy of Sciences viewed the progress of fabrication and employment of cellulose-based fluorescent materials in recent years, and summarized the functions of cellulose as well as the sensing mechanism of fluorescent materials. In particular, the perspective of cellulose-based fluorescent materials for sensing are discussed from the design and functionality perspectives, and the future opportunities for the development of this material system are analyzed to promote its more advanced sensing applications through improved scalability and multifunctionality. This review, titled "Cellulose-based fluorescent materials for chemical sensing applications", was published in Coordination Chemistry Reviews. Dr. LIU Yali is the first author, and Prof. ZU Baiyi and Prof. DOU Xincun are the corresponding authors.
Researchers reviewed the work on the preparation and application of cellulose-based fluorescent materials published in the past two decades. Based on a series of cellulose-based fluorescent sensing solutions developed by the team during the long-term research on visual, highly sensitive, rapid identification of harmful chemicals (Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, e2300526;Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 33, 11679; Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2002991; Adv. Opt. Mater. 2020, 8, 2000524; Anal. Methods 2022, 14, 4485), this review was carried out from four aspects: the structural characteristics of cellulose and its derivatives, the preparation strategies of cellulose-based fluorescent materials, the roles of cellulose and its derivatives in fluorescent sensing materials, and the sensing applications of cellulose-based fluorescent materials. Finally, the research trends in the optimization of the fluorescence performance of cellulose-based fluorescent sensing materials, the breakthrough of the sensing mechanism, large-scale production, and the expansion of practical applications were analyzed, and the development prospects in the field of advanced fluorescent sensing were prospected. This review is helpful for integrating knowledge and technologies from different disciplines including materials science, chemistry, and biology, promoting interdisciplinary integration. It will surely attract more and more attention and provide guidance for the development of green and sustainable optical sensors.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, Tianshan Innovation Team Plan, the Youth Innovation Promotion Association, CAS, and the Scheme of Tianchi Talent on Doctor Introduction in Xinjiang.
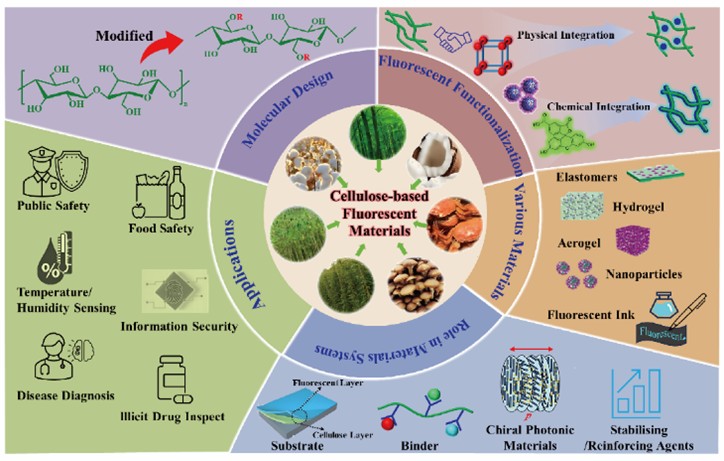
Figure: Fabrication and application of cellulose-based fluorescent assembly materials (lmage by Prof. DOU Xincun 's group).
附件下载:
 (86) 991-3838931
(86) 991-3838931 lhskj@ms.xjb.ac.cn
lhskj@ms.xjb.ac.cn (86)991-3838957
(86)991-3838957 40-1 Beijing Road
Urumqi, XinjiangChina
40-1 Beijing Road
Urumqi, XinjiangChina