Research Progress in on Nano-Gel Wound Healing with Schizonepeta annua Essential Oil
Editor: | Jun 26,2025
Schizonepeta annua is a traditional medicinal plant whose essential oil is rich in active components such as thymol and carvacrol. It is not only a spice of significant commercial and agricultural value but also a traditional Chinese herb with medicinal properties such as warming the middle and dispelling cold, as well as relieving pain.
Despite its long history of medicinal use, the application of Schizonepeta annua essential oil in wound healing remains underexplored. Chronic wound healing is a major global healthcare challenge, affecting over 40 million patients annually and incurring medical costs exceeding $25 billion in developed countries. Bacterial infections severely hinder the healing process, and the growing issue of antibiotic resistance has made the development of new antimicrobial agents an urgent priority. While natural essential oils possess multiple biological activities, including antibacterial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory effects, their clinical application has been limited by challenges such as high volatility and poor stability.
The Ethnic Medicine Research and Innovation Team at the Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, led by Researcher Haji Akber Aisa, has successfully developed a thermosensitive nano-emulsion gel wound dressing system loaded with Schizonepeta annua essential oil. Through systematic optimization, the team prepared a stable oil-in-water nano-emulsion, achieving uniform nanoparticles. The gel exhibits ideal wound application characteristics, including temperature-responsive gelation, excellent shear-thinning behavior, and an erosion-controlled release mechanism. In vitro antibacterial experiments demonstrated that the gel effectively combats key wound pathogens, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), while showing good biocompatibility with keratinocytes at antibacterial-effective concentrations. In a rat burn model, the gel treatment group significantly promoted epidermal regeneration, improved collagen tissue organization, and effectively regulated inflammatory marker levels. This study combines natural antibacterial components with biocompatible materials, offering a promising platform for advanced wound management and providing a natural alternative to traditional antibacterial dressings with superior healing-promoting capabilities.
The related findings were published under the title "Development and evaluation of a thermosensitive nanoemulsion hydrogel loaded with Schizonepeta annua essential oil for enhanced wound healing" in Industrial Crops and Products. Cheng Feng, a Ph.D. candidate at the Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, served as the first author, with Researcher Maiwulanjiang Maitinuer as the corresponding author. The Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry was the primary affiliation. This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China and Xinjiang Tianshan Talents Program.
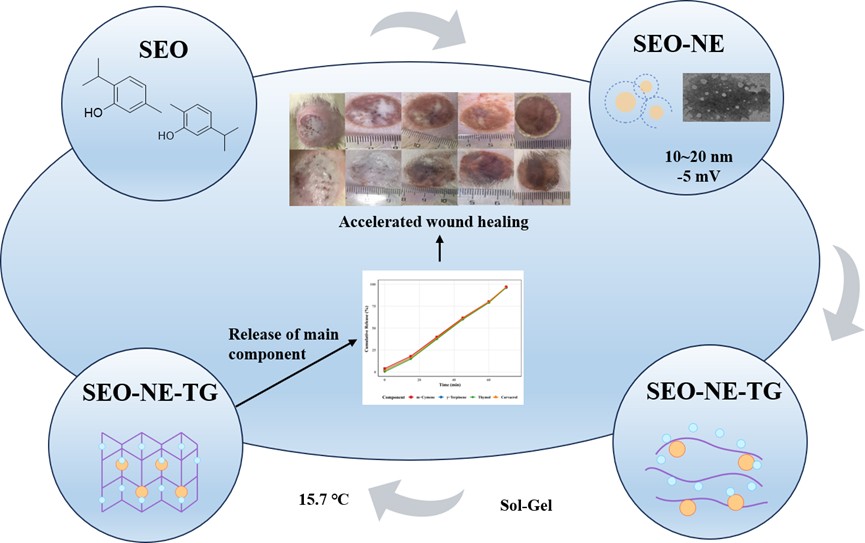
Schematic diagram of Schizonepeta annua essential oil nano-gel preparation and wound healing study
附件下载:
 (86) 991-3838931
(86) 991-3838931 lhskj@ms.xjb.ac.cn
lhskj@ms.xjb.ac.cn (86)991-3838957
(86)991-3838957 40-1 Beijing Road
Urumqi, XinjiangChina
40-1 Beijing Road
Urumqi, XinjiangChina