Highly Conductive Cu-deposited Basalt Fiber Fabric for High-performance Electromagnetic Interference Shielding and Joule Heating
Editor: | Jun 30,2025
With the evolution from 5G to 6G technology, the miniaturization and high performance of electronic devices have led to increased electromagnetic radiation, which poses threats to device reliability and human health. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop ultra-thin, flexible, transparent, durable, and lightweight EMI shielding materials. Traditional transition metal nanoparticles and their alloys, although having good conductivity, still have problems such as insufficient mechanical strength and poor corrosion resistance in EMI shielding applications.
To overcome these limitations, Prof. Abudukeremu Kadier and Prof. Peng-Cheng Ma’s group at the Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry (XTIPC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has successfully developed a Cu-deposited BFF material using electroless copper plating technology. This material achieves an EMI shielding effectiveness of 81.7 dB in the X band (8.2–12.4 GHz) at a thickness of approximately 7.69 mm. Its electrical conductivity can reach up to 4.81×105 S m-1, and its density is only 3.08 g cm-3, significantly lower than that of bulk copper (8.96 g cm-3). In addition, at 50 oC, the material exhibits excellent mechanical properties, with breaking forces of 3343 N (warp) and 665 N (weft). Practical tests have shown that the Cu-deposited BFF can achieve an efficient Joule heating effect, reaching 136 oC at 1.0 V. The material maintains superior EMI shielding and stability at room temperature and under simulated natural conditions. This achievement not only provides critical technological support for advanced wireless electronic devices and next-generation communication technologies such as 6G but also promotes the development of EMI shielding materials and opens up new avenues for the application of electronic textiles and electromagnetic shielding technologies.
The research results have been recently published in the international journal Materials Chemistry Frontiers. The Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, is the sole corresponding unit. Assistant researcher Parkash Anand is the first author, and researchers Abudukeremu Kadie and Ma Pengcheng are the corresponding authors. The study was supported by several funding programs, including the Tianchi Doctor Program of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, the Tianshan Elite Talent Program of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, and the Western Light Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
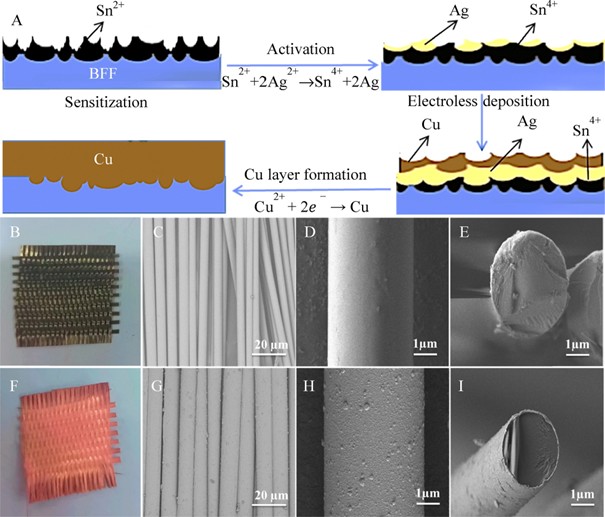
Figure 1. Fabrication strategy and surface morphology analysis: (A) schematic illustration of the mechanism of electroless Cu deposition on BFF; (B) pristine BFF; (C)–(E) SEM images of pristine BFF; (F) Cu-deposited BFF at 50°C; and (G)–(I) SEM images of Cu-deposited BFF at 50°C.
附件下载:
 (86) 991-3838931
(86) 991-3838931 lhskj@ms.xjb.ac.cn
lhskj@ms.xjb.ac.cn (86)991-3838957
(86)991-3838957 40-1 Beijing Road
Urumqi, XinjiangChina
40-1 Beijing Road
Urumqi, XinjiangChina