Progress in the Research of Ultraviolet Nonlinear Optical Crystals in Rare Earth Borate Fluorides Containing [B3O6] Units
Editor: | Nov 03,2025
Nonlinear optical (NLO) materials are at the core of modern photonic technology,facilitating the advancement of innovative applications such as laser frequency conversion, ultrafast optical switching, and quantum information processing. Among the wide variety of NLO crystals, borate systems have consistently been at the forefront of short-wavelength (<280 nm) NLO materials due to their excellent structural adaptability, wide transparency window, and high laser damage threshold. Notable examples of such crystals including KBe2BO3F2, β-BaB2O4, and LiB3O5 have significantly contributed to and continued to lead the global development of NLO crystals. Nevertheless,the development of next-generation NLO materials still encounters a critical challenge: adequate birefringence for achieving short-wavelength phase-matching while maintaining strong second-harmonic generation (SHG) effect. Researches indicate that the synergistic interactions among various anions (e.g., O2-, F-, BO33-, BO3F4-, etc.) can unleash unprecedented optical functions. Concurrently, the planar π-conjugated [B3O6] group exhibits a large hyperpolarizability and high polarizability anisotropy, facilitating efficient SHG and sufficient birefringence for short-wavelength phase-matching.
The Research Center for Crystal Materials of the Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has been engaged in the research of novel UV and deep-UV borate optoelectronic functional crystals for a long time. Guided by a synergistic optimization strategy, the team successfully synthesized three novel rare-earth metal borate fluorides, K2GdB3O6F2, Rb2LuB3O6F2 and Cs2LuB3O6F2. All the three title compounds exhibit short cutoff edges less than 200 nm, with Cs2LuB3O6F2 displaying an large experimental frequency doubling effect of 1.5 × KH2PO4. The type-Ⅰ shortest phase-matching wavelengths for Rb2LuB3O6F2 and Cs2LuB3O6F2 are evaluated to be 210 and 202 nm, respectively, indicating their potential for direct output of 213 coherent lights through a fifth harmonic generation process of Nd: YAG laser. Significantly, a structural evolution from centrosymmetric K2GdB3O6F2 to non-centrosymmetric Rb2LuB3O6F2 and Cs2LuB3O6F2 reveals that the arrangement and orientation of the [B3O6] groups are seriously affected by the rare earth metal polyhedral coordination, which plays a decisive role in the symmetry of the structure.
This research was published in Adv. Funct. Mater. in the form of Research Article (Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, e20516), with researchers Shilie Pan and Yun Yang of Research Center for Crystal Materials as the corresponding authors, and the Ph.D graduate student Qianzhen Zhang as the first author. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang, etc.
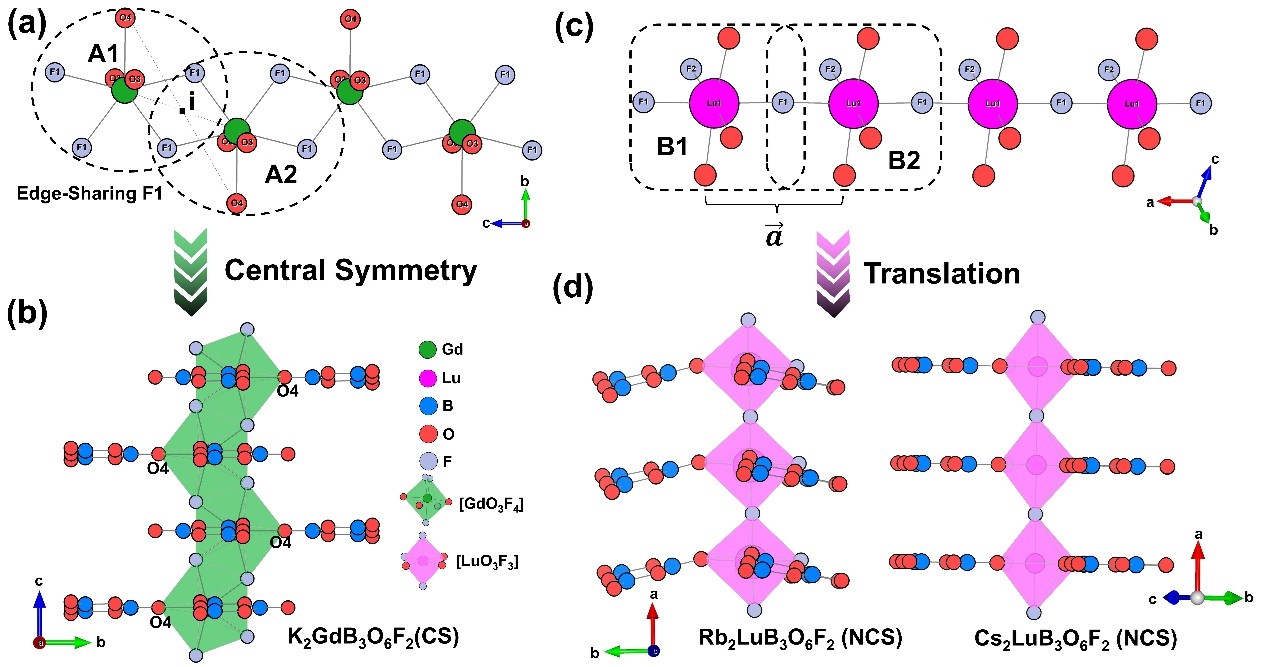
Coordinate sensitivity of the [B3O6] groups in centrosymmetric and non-centrosymmetric structures
附件下载:
 (86) 991-3838931
(86) 991-3838931 lhskj@ms.xjb.ac.cn
lhskj@ms.xjb.ac.cn (86)991-3838957
(86)991-3838957 40-1 Beijing Road
Urumqi, XinjiangChina
40-1 Beijing Road
Urumqi, XinjiangChina