Research Progress in Sulfate DUV Birefringent Crystals
Editor: | Nov 14,2025
Recently, the Research Center for Crystal Materials of the XTIPC has achieved new progress in the research on sulfate deep-ultraviolet (DUV) birefringent crystals. By introducing rare earth metal Y3+ cations into alkali metal sulfates, the team successfully obtained six new sulfate crystals, significantly improving the birefringence in this system. This research provides a new idea for the development of novel sulfate DUV optical crystals.
Birefringence is an important optical property of crystalline materials, which exhibit anisotropic refractive indices for polarized light. It plays a crucial role in modern optoelectronic technologies such as integrated optical modulators, electro-optical switches, and nonlinear optical frequency conversion. However, there are relatively few materials that simultaneously exhibit high birefringence and DUV transmission. Sulfates are considered ideal candidate systems for DUV optical materials due to the wide energy gap of their [SO4] tetrahedral groups. Nevertheless, the low polarizability anisotropy of the [SO4] tetrahedral structure severely limits the further improvement of the birefringence in sulfate systems.
The team introduced rare earth metal Y3+ cations with an f0 electronic configuration into traditional alkali metal sulfates, and successfully designed and obtained six compounds of the types AY(SO4)2 and A3Y(SO4)3 (A = K, Rb, and Cs). Structural analysis shows that Y3+ forms highly distorted [YOn] polyhedra (n = 7, 8), which construct a Y–O–S network structure with adjustable dimensionality together with [SO4] tetrahedra. As the radius of the alkali metal cation increases, the Y–O–S frameworks gradually transform from three-dimensional structures to approximately two-dimensional layered structures, significantly enhancing the optical anisotropy. Theoretical calculations indicate that the birefringence of these compounds ranges from 0.013–0.056@546 nm, with the highest value reaching 25 times that of the corresponding parent alkali metal sulfates. This result is superior to that of most reported sulfate DUV crystals. Meanwhile, all compounds maintain an absorption edge below 200 nm, meeting the requirements for DUV applications. This research realizes a substantial enhancement of birefringence in DUV sulfates and provides an approach for the subsequent design of high-performance sulfate DUV birefringent crystals and nonlinear optical crystals.
This research has been published in Chemistry of Materials (Chem.Mater.2025, DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.5c02373), with Prof. Shilie Pan and Prof. Fangfang Zhang of the Research Center for Crystal Materials as the corresponding authors, and the Doctoral student Luyong Zhang as the first author. This work was supported by the Tianshan Innovation Team Program, the CAS Youth Interdisciplinary Team Program, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Tianshan Talent Training Program, the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the Xinjiang Major Science and Technology Project.
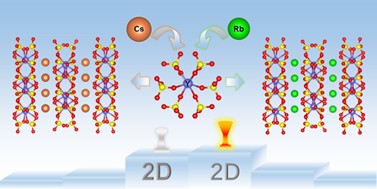
Cation-Regulated Y–O–S Layered Structures Achieve Substantial Enhancement of Birefringence
附件下载:
 (86) 991-3838931
(86) 991-3838931 lhskj@ms.xjb.ac.cn
lhskj@ms.xjb.ac.cn (86)991-3838957
(86)991-3838957 40-1 Beijing Road
Urumqi, XinjiangChina
40-1 Beijing Road
Urumqi, XinjiangChina