Infrared nonlinear optical (NLO) crystals have been developed as the critical materials to achieve the efficient IR laser output by the typical frequency-conversion technology and applied in military and civil fields. However, commercial IR NLO materials are seriously limited in the IR region because of their low laser-damage thresholds (LDTs) or harmful two-photon absorption (TPA). Therefore, the discovery of new IR NLO materials with optimal key performances (concurrently large NLO coefficient (dij) and wide optical bandgap (Eg)) has become imperative. Moreover, the efficient design strategy turns to be very important to direct the studies in the future. Pan group in Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry have studied IR NLO materials for many years, in this review, the structure-performance relationship for 49 compounds is focused on and the results show that alkali or/and alkalineearth metals must be the preferred cations to maintain the wide Eg. Besides, their critical anionic groups are summarized and shown as follows: (i) typical tetrahedral MIIIQ4 (MIII = Ga, In) or/and MIVQ4 (MIV = Si, Ge; Q = S, Se) or PS4 units; (ii) d10 elements-centered (MIIQ4: MII = Zn, Cd) and typical MIIIQ4 or MIVQ4 tetrahedra; (iii) halogen-centered polyhedral ligands. So the combination of above anionic groups and alkali or/ and alkaline earth metals into crystal structures produces the feasible design strategy to explore new IR NLO materials with excellent performances. Paper Link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0010854518303187 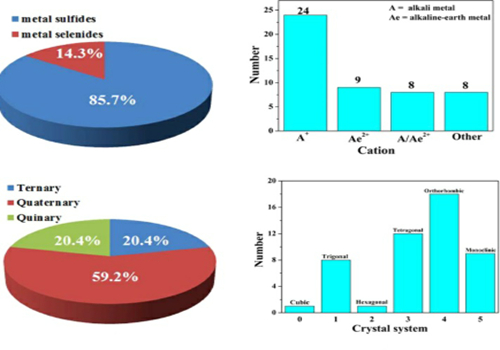
|
