Exploration of new infrared (IR) nonlinear optical (NLO) materials is still in urgency owing to the indispensable roles in optoelectronic devices, resource exploration, and long-distance laser communication. The formidable challenge is to balance the contradiction between wide band gaps and large second harmonic generation (SHG) effects in IR NLO materials. Currently, the IR NLO candidate materials can be divided into the following five types: chalcogenides, halides, oxyhalides, oxides, and chalcohalides. Among them, chalcogenides are the most exploratory system as IR NLO materials since they usually display outstanding IR NLO performances. The chalcohalides which feature the mix of sulfur and halogen in a non-centrosymmetric coordinated environment can induce IR NLO performance. Compared with traditional chalcogenides, the development and exploration of chalcohalides in the mid-IR NLO field have not been received systematic research and attention. Up to now, based on the investigation of inorganic crystal structure database (ICSD, Version 4.3.0 build 20191115-0733) 45 noncentrosymmetric chalcohalides are found, and by the density functional theory and high-throughput screening methodology, structures and optical properties of the chalcohalides are summarized and investigated. The results indicate that the chalcohalides would be potential applications in mid-IR NLO materials. Introduction of the halogen atoms with a large electronegativity into chalcogenides will increase their band gaps, and the coordination polyhedra could be more distorted owing to the difference of bond length which is beneficial to large second harmonic generation (SHG) responses. The results indicate that the transition metal chalcohalides exhibit strong SHG responses when the asymmetric units with large distortion are aligned uniformly. The adduct-type chalcohalides and Lewis acid adduct chalcohalides that contain novel isolated rings can have large birefringence. In particularly, a series of alkali metal chalcohalides are highlighted owing to their good mid-IR NLO properties involving wide band gaps and large NLO coefficients. All the results suggest that the chalcohalides are potential systems in exploring new mid-IR materials. The work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China,the Western Light Foundation of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Tianshan Innovation Team Program. Link: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2020.213379 
Figure 1 Five types of the common IR NLO candidate materials. 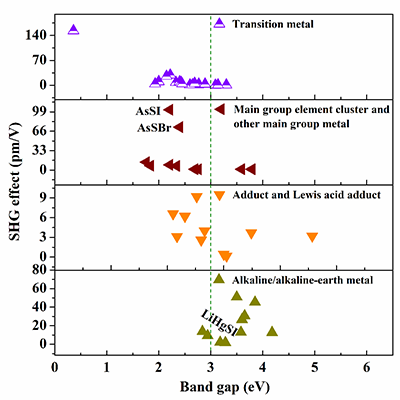
Figure 2 The distributions of all the mentioned chalcohalides in terms of band gaps and calculated the largest NLO coefficients in effective coefficients in this review. |
