With the increasing popularity of lithium ion battery application, new technical requirements emergy. However, low temperature performance of cathode material directly limits the environmental adaptability of the lithium-ion battery, thus affecting the promotion and application of lithium-ion battery. The lithium-ion battery operating temperature is generally between -20~55 °C, and even up to -40~55 °C in some special field .
In order to effectively improve the low temperature performance of cathode material for lithium-ion, Prof. KANG Xueya’s research group at Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry, CAS, carried out a systematic study on the low-temperature properties of LiFePO4/C and Li3V2(PO4)3/C. The study analyzed the relationship between materials properties and temperature, and identified the key factors affecting the material temperature characteristics.
Results showed that the electrochemical performances of the samples were closely related with the temperature, the lower the operation temperature was, the poorer the performances were. There was a nonlinear relationship between the performance and temperature, which should be attributed to the nonlinear change of Rct, DLi and σLi with temperature.
And a new synthetic process was used to develop a series of xLiFePO4·yLi3V2(PO4)3/C composite cathode material. Due to the two-phase composite effect and element doping effect, the low-temperature performance of xLiFePO4·yLi3V2(PO4)3/C was significantly improved than LiFePO4/C.
The result was publishedon Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry, 2012, 16:1917-1923. The paper can be also archived at http://www.springerlink.com/content/v0p5p1541p2296u6/.
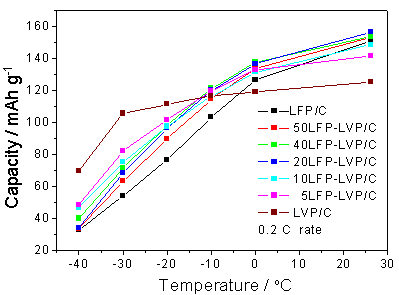
Capacity-temperature curves of different samples under 0.2 C rate
