The generation of deep-UV coherent light from nonlinear optical (NLO) materialsas one of the most promising resource, has become a topic of intensive study due to its important applications in a broad range of fields, such as semiconductor photolithography, laser micromachining, photochemical synthesis and material processing.Although considerable progress has been made recently in the exploration of new NLO materials, many of them based on oxides such as the famous β-BaB2O4 (BBO) and LiB3O5 (LBO), which have widely been used as optoelectronic devices, can not be used in deep-UV region because of a limited UV-transparent range and birefringence problem, respectively.
The search of new nonlinear optical (NLO) materials with some properties, namely, large NLO coefficient, wide transparency range, good chemical and mechanical stability is a hot topic. A comprehensive analysis of structure-property relationship is vital importance. Therefore, the design and synthesis of NLOmaterials is still one of the most interesting and challenging goals of the chemistry and materials science field.
Prof. PAN Shilie with his team from Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences (XTIPC), and American scientist, Professor Kenneth R. Poeppelmeier, recently discovered new UV NLO material systems based on borosilicate.In the B-rich borosilicate, the B-O basic units can condense to form the large B-O groups. The relative large B-O groups are more flexible than single SiO4 tetrahedron. Therefore, when the large B-O groups are connected with SiO4 tetrahedra to form three-dimensional (3D) framework, they are easily pulled to generate the large distortions(Fig.1). Guide by the idea, a novel borosilicate, Cs2B4SiO9 was synthesized. It possesses the powder SHG response about 4.6 times that of KH2PO4 (KDP), which is the strongest among borosilicate to date, and is phase-matchable(Fig.2). In addition, it's worth noting that Cs2B4SiO9 exhibits the short UV cutoff edge (below 190 nm). These results indicate that the Cs2B4SiO9 crystal may be a promising NLO material in the deep-UV region and B-rich borosilicate may be a new field for the study of deep UV NLO materials.
The results as a communication titled Cs2B4SiO9:A Deep-UV Nonlinear Optical Crystal, have been published on Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. (DOI: 10.1002/anie.201209151).
The work has been supported by Chinese Academy of Sciences, the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
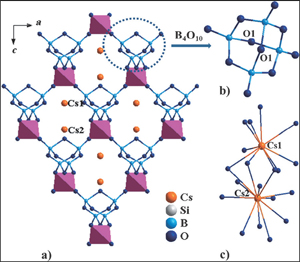
Fig.1. The 3D framework of Cs2B4SiO9(Cs-O bonds omitted for clarity )
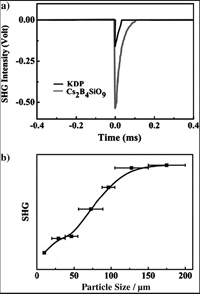
Fig. 2. SHG intensities of Cs2B4SiO9 and phase-matching curve of Cs2B4SiO9
Contact:
Prof.PAN Shilie
Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry
Chinese Academy of Sciences
E-mail:slpan@ms.xjb.ac.cn
