Hydrocarboxylation of olefins as one of the important methods for the functionalization of olefinic double bond, is a very promising and environmentally friendly method for obtaining carboxylic acids.Palladium-phosphine(Pd-P) complexes have been widely used as the catalysts in hydrocarboxylation of olefins due to their high activity and selectivity under mild conditions. Water-soluble phosphine ligands, such as TPPTS(trisulfonated triphenylphosphine), can keep the Pd-P complexes in aqueous phase to realize the recycle and reuse of the catalysts.
Researchers from Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences (XTIPC) found the promoting effects of alkali halides including MCl, MBr, MI on hydrocarboxylation of styrene. Researchers explored the effects of different alkali metal halide salts on the yield of acids, selectivity of products, and catalytic stability for the hydrocarboxylation of styrene by using Pd-TPPTS catalytic system (Fig.1). Among those alkali halides, MBr was the best promoter. Based on 31P NMR and 1H NMR spectra results, it was found that alkali metal halide salts could stabilize the Pd(II) species, and styrene was coordinated and activated with Pd center even at room temperature, which implied the rate-limiting step for this reaction should be the following ones, like CO insertion or nucleophilic attack by H2O. Besides, the halide anions take a vital role in obtaining the linear product.
In view of reaction activity and selectivity for addition of alkali metal halide in hydrocarboxylation, researchers proposed the mechanism of the hydrocarboxylation catalyzed by Pd(II) and Pd(0) species. According to the present catalytic system, the presence of halide salt can stabilize Pd(II)-TPPTS species and thus favored the formation of the linear acids(Fig2).
The results have been published on Catalysis Letters,2013, 143(3):289-297. The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and One Hundred Person Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
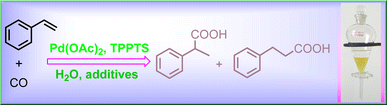
Fig 1. Hydrocarboxylation of styrene catalyzed by Pd-TPPTS

Fig 2. The possible mechanism of hydrocarboxylation of styrene catalyzed by Pd(0) (1) and Pd(II) species (2), respectively.
