Graphene quantum dots (GQDs) with excellent properties of graphene, quantum confinement and bounder effect have attracted more attention of scientists. However, controllable preparation of GQDs with uniform particle size and strong dispersity is still a challenge in the field of GQDs.
Researchers at Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry (XTIPC), Chinese Academy of Sciences, have developed a novel top-down approach to synthesize a high-yield preparation of GQDs.
In the study, a high-yield (48%) preparation and a facile separation of yellow-luminescent GQDs have been synthesized by using a pre-made carbon replica (C/SBA-15) of SBA-15 as a nanoreactor and HNO3 vapor cutting strategy. Researchers found that the as-prepared C/SBA-15 containing ordered mesopores may be used as the promising raw material for preparation of GQDs with controllable sizes, due to its confined mesoporous structures and filling graphitic carbons. The obtained GQDs containing abundant oxygen-containing groups (ca. 30% for oxygen content) showed a narrow size distribution (2.5-5.2 nm), good water solubility, good photostability and high selectivity for Fe(III) sensing in tap water with satisfying recovery.
Inspired by the external oxygen-containing groups of the GQDs, researchers investigated their application as fluorescent probes for Fe(III) determination in tap water based on a calibration curve of Fe(III) standards of different concentrations. However, the results of Fe(III) determination showed that the obtained GQDs exhibited a high selectivity towards Fe(III), with satisfying recoveries ranging from 94.3% to 106%.
Based on the experiments, it indicated that Cu(II), Co(II), Mn(II), Ni(II) could also quench the fluorescence of the as-prepared GQD after its surface states being adjusted, which might presage more possible applications of this material.
The results have been published in Carbon, Volume 87, 2015, Pages 215–225. This work was supported by the Hundred Talent Program and the Western Light Program from Chinese Academy of Sciences, National Natural Science Foundation of China, etc.
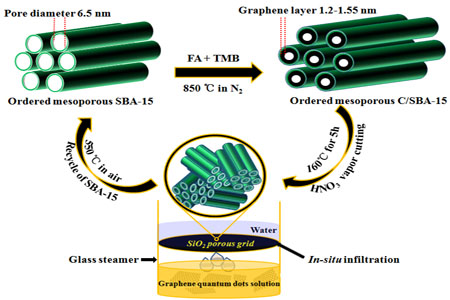
Schematic diagram of the preparation of GQDs
Contact:Prof.YUAN Qunhui
E-mail:yuanqh@ms.xjb.ac.cn
Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry
