Photocatalytic reduction of CO2 with H2O vapor on TiO2 has attracted more attention because it is a promising “green chemistry” way for the direct conversion of CO2 to value-added fuels (CO, methane, methanol, etc.) driven by sunlight. However, the drawback in weak interaction between TiO2 and CO2 molecules limited CO2 photoreduction.
A research team led by Prof. WANG Chuanyi at Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry of Chinese Academy of Sciences employed ceria as a basic promoter to strengthen the interaction of CO2 with photocatalyst surface and fabricated highly dispersed CeO2/TiO2 and bare TiO2 catalysts.
Researchers prepared highly dispersed CeO2 on TiO2 catalysts by a one-pot hydrothermal method using titanium (IV) bis (ammonium lactate) dihydroxides as Ti source and Ce(NO3)3•6H2O as Ce source, respectively. They found the presence of CeO2-x and ceria−titania interfaces in CeO2-x/TiO2 catalysts strengthens the bonding of CO2 with catalyst surfaces and increases the production of b-CO32− and b-HCO3− species. The process was different from m-CO32−, b-CO32− and b-HCO3− surface species, which could be easily transformed to surface CO2− in the presence of H2O under simulated sunlight irradiation.
Based on the microcalorimetric measurement and in situ infrared spectroscopy (IR), the results showed that the strengths and states of CO2 adsorption and the course of photoreduction of CO2 with H2O vapor.
The research team proposed for the first time experimentally that the surface CO2− species is derived from b-CO32− and b-HCO3− but not from gaseous and physisorbed CO2 molecules.
The study deepens the understanding of the role of ceria in CO2 photoreduction at TiO2 catalysts and the course of catalysis of CO2 photoreduction in the presence of H2O vapor. It has been published in Journal of Catalysis.
The work was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China, the CAS Hundred Talent Program, the CAS-SAFEA International Partnership Program for Creative Research Teams, etc.
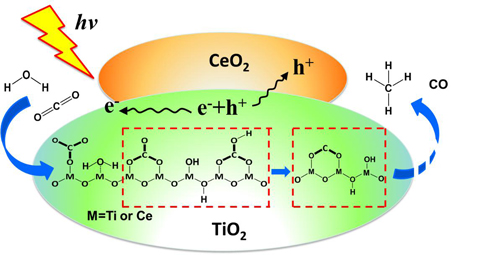
Figure: A scheme of route for CO2 photoreduction with H2O vapor (Image by XTIPC)
Contact:
Prof. WANG Chuanyi
E-mail:cywang@ms.xjb.ac.cn
Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry,CAS
