Infrared (IR) nonlinear optical (NLO) materials play a very important role in many fields, including medicine, scientific research, civil and military industries etc. Large amounts of efforts have been made to discover new excellent materials because the own drawbacks (low laser damage threshold and two-photon absorption) of commercially applied IR NLO materials AgGaQ2 (Q = S, Se) and ZnGeP2 have hindered their further application.
To obtain the material with good balance between the large NLO coefficient (dij) and wide band gap (Eg), a research group led by Prof. PAN Shilie at Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry of Chinese Academy of Sciences proposed a new design strategy that combines the easily distorted GeS4 ligands with alkali metal (Na) and Zn element with d10 configuration to prepare the new IR NLO material.
Guided by the above design strategy, researchers successfully synthesized a new IR NLO material Na2ZnGe2S6 by the solid-state reaction technique in a vacuum-sealed silica tube. Based on systematic properties investigations, this material shows excellent potential as IR NLO candidate, including the wide transparent range from 0.38 to 22 μm, large SHG response (0.9 times that of AgGaS2 at 2.09 μm), high laser damage threshold (6 times that of AgGaS2) and good chemical stability. The material satisfy the balance condition of dij = ~30 × KDP and Eg = 3.25 eV, which also indicate that it can be expected to avoid the drawbacks of commercial IR NLO materials.
Moreover, researchers found that this material has the infinite common-vertex linked [GeS3]n chain-like structure, which is rarely discovered among the known alkali-containing thiogermanides.
The result was published in J. Am. Chem. Soc.
This work was also supported by the Western Light Foundation of Chinese Academy of Sciences and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
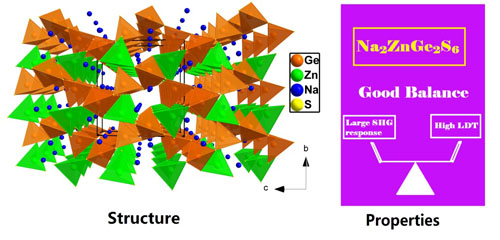
Figure:Structure and properties of Na2ZnGe2S6(Image by LI Guangmao)
Contact:
Prof. PAN Shilie
E-mail: slpan@ms.xjb.ac.cn
Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry,CAS
