Graphene holds great application potential in energy, catalysis and environment fields due to its unique physical and chemical properties. Recently, the adsorption of phenol based organic pollutants by graphene-based material has drawn considerable attention. Oxygen-containing functional groups on the surface of graphene based material can form hydrogen bonds with phenol based contaminants.
However, the adsorption mechanism of phenol based contaminants on reduced graphene oxides and the effect of the reduction degree of reduced graphene oxides on the adsorption of phenol based contaminants on reduced graphene oxides have been rarely reported. Graphene base material has a small size and excellent dispersibility in water, which makes it difficult to separate, collect and recycle after use.
The research group led by Prof. ZHANG Yagang at Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry (XTIPC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences designed and synthesized magnetic reduced graphene oxides for phenol type contaminants which feature easy and fast separation by applying magnetic field and reusable.
Researchers systematically investigated the reduction process of the graphene oxide and synthesized magnetic reduced graphene oxide materials with different reduction degree.They also explored the effects of the reduction degree of graphene oxide on the adsorption kinetics and adsorption capacity of bisphenol A on magnetic reduced graphene oxides. The results showed that the deep reduction of graphene oxides decreases its adsorption capacity for bisphenol A.
However, after normalized by material's specific surface area, the deep reduction of graphene oxides can enhance the adsorption capacity per material's specific surface area of bisphenol A on magnetic reduced graphene oxides.
Based on the experimental results, researchers proposed the mechanism of bisphenol A absorbed on graphene based material: the π-π interaction plays major role in the process of adsorption of bisphenol A and after deep reduction of graphene oxides, the adsorption capacity of bisphenol A is decreased due to the decrease of the adsorption sites caused by the aggregation of graphene sheets.
Furthermore, results showed that the reduced graphene oxides after magnetic functionalization can be quickly collected by external magnetic field and used repeatedly after regeneration, which lays a strong foundation for large-scale industrial application.
The study was published in RSC Advances.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Thousand Talent Program.
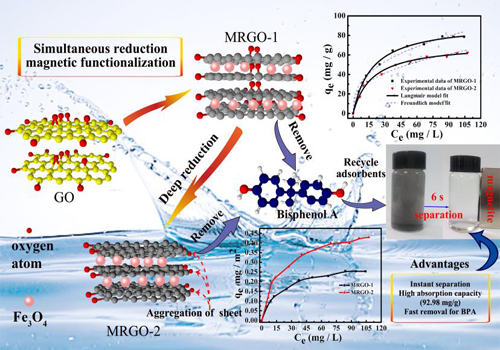
Figure:Cartoon shows magnetic reduced graphene oxide composites (MRGO) with different reduction degree for removal of Bisphenol A from aqueous solution.(Image by XTIPC)
Contact:
Prof. ZHANG Yagang
E-mail:ygzhang@ms.xjb.ac.cn
Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry,CAS
