Deep-ultraviolet (DUV, wavelength λ<200 nm) nonlinear optical (NLO) materials are crucial in producing solid-state lasers and stimulates great interests because of its wide range of applications in the semiconductor industry.
KBe2BO3F2 (KBBF) is an unique NLO material that can efficiently generate DUV light but with a strong layer growth habit and toxicity issue of containing beryllium that restrict its applications. Therefore, the exploration and development of the next generation DUV NLO materials is in great importance.
Recently, a team led by Prof.PAN Shilie at Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry(XTIPC) of Chinese Academy of Science designed and prepared a promising DUV NLO material, NH4B4O6F (ABF), which owns favorable NLO properties comparable to famous KBBF crystal. The study was published in J. Am. Chem. Soc.
In this study, [BO3F] is substituted for [BeO3F] and the NH4+ ionic group is substituted for K cation. ABF was found to perfectly inherit the excellent structure features of KBBF, and exhibit a wide DUV transparency window with a cutoff edge down to 156 nm, a large NLO efficiency (3 × KDP), and suitable birefringence that enable simple frequency doubling below 200 nm (as short as 158 nm).
Compared with KBBF, this material has a compact structure with enhanced interlayer binding forces. Researchers obtained up to the centimeter-level bulk crystals. In addition, ABF can be made with an environment-friendly synthesis process without using highly toxic beryllium oxide powders. These optimizations reduce the health risk during crystal growth and are beneficial to industrial applications –insurmountable problems facing KBBF.
Besides, researchers found that ABF exhibits a NLO efficiency about 2.5 times that of KBBF. Since the conversion efficiency is proportional to the square of deff, ABF will possess much higher performance than KBBF in DUV frequency conversion process. All those properties make ABF an ideal candidate of next generation DUV NLO material.
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China, National Key Research Project, and Xinjiang Key Research and Development Program.
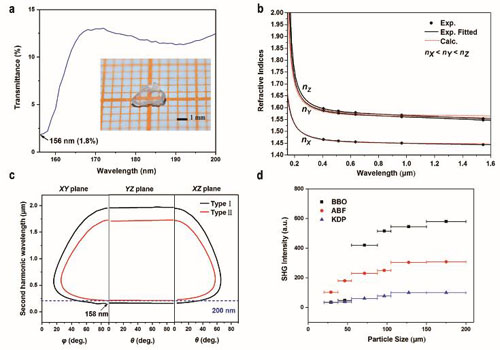
Figure: (a) DUV transmission spectrum on single crystal of ABF. (b) Experimental and calculated results of refractive indices. (c) Phase-matching conditions of ABF. (d) Powder SHG measurements at 1064 nm. (Image by XTIPC)
Contact:
Prof.PAN Shilie
E-mail:slpan@ms.xjb.ac.cn
Xinjiang Technical Institute of Physics & Chemistry, CAS
